The Wonders of Indian Gooseberry (Amla): A Comprehensive Exploration – By Nadeeka – eLanka
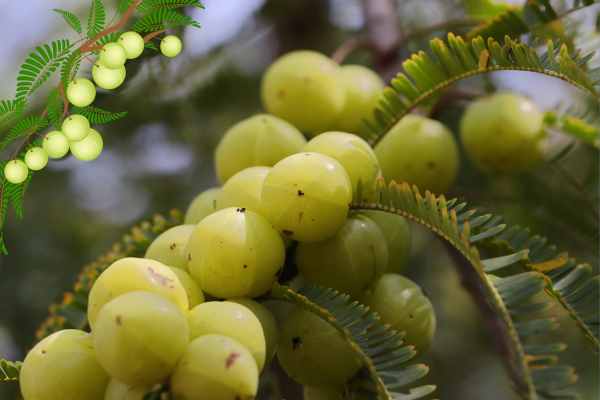

The Indian gooseberry, scientifically known as Phyllanthus emblica, and commonly referred to as amla or nelli, is a small, greenish-yellow fruit that has been treasured for centuries in various cultural and medicinal contexts. Renowned for its potent health benefits and rich nutritional profile, amla is celebrated not only in Ayurveda but also in modern scientific research for its therapeutic properties. This article delves deeply into the history, nutritional composition, health benefits, and various uses of Indian gooseberry, highlighting why this remarkable fruit deserves a prominent place in our daily lives.
A Historical Perspective
The history of Indian gooseberry is deeply intertwined with the cultural and medicinal traditions of India. References to amla can be found in ancient Ayurvedic texts dating back over 3,000 years. It is described in the Charaka Samhita and Sushruta Samhita, two foundational Ayurvedic texts, where it is extolled for its rejuvenating and healing properties. In Hindu mythology, the amla tree is considered sacred, believed to have originated from the drops of amrita, the nectar of immortality.
Amla has also been utilized in various traditional medicinal systems outside India, including Unani and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Its widespread use across different cultures underscores its importance and versatility as a medicinal fruit.

Nutritional Composition
Indian gooseberry is a nutritional powerhouse, packed with an impressive array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. A 100-gram serving of fresh amla provides approximately:
- Calories: 44
- Protein: 0.9 grams
- Carbohydrates: 10 grams
- Fiber: 4.3 grams
- Vitamin C: 27.7 mg (46% of the Daily Value)
- Vitamin A: 290 IU
- Calcium: 25 mg
- Iron: 0.31 mg
One of the most remarkable features of amla is its extraordinarily high vitamin C content. In fact, amla contains more vitamin C per gram than oranges, making it one of the richest natural sources of this vital nutrient. Additionally, amla is rich in polyphenols, tannins, and flavonoids, which contribute to its potent antioxidant properties.
Health Benefits
The health benefits of Indian gooseberry are extensive, owing to its rich nutritional composition. Here are some of the key benefits supported by scientific research and traditional knowledge:
- Immune System Support: The high vitamin C content in amla plays a crucial role in enhancing immune function. Vitamin C is known to stimulate the production and activity of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. Regular consumption of amla can help protect against common colds, flu, and other infections.
- Antioxidant Properties: Amla is a potent antioxidant, helping to neutralize free radicals that cause oxidative stress and damage to cells. The presence of polyphenols, tannins, and flavonoids further enhances its ability to protect against cellular damage, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
- Digestive Health: Amla is an excellent source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes regular bowel movements. It also has mild laxative properties, making it effective in relieving constipation. Additionally, amla stimulates the production of gastric juices, enhancing appetite and aiding in the absorption of nutrients.
- Heart Health: Regular consumption of amla has been linked to improved heart health. The antioxidants in amla help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are major contributors to heart disease. Amla has been shown to lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries, thereby reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Diabetes Management: Amla has been traditionally used to manage diabetes due to its ability to lower blood sugar levels. Research indicates that amla can enhance insulin secretion and improve glucose metabolism, making it beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. The high fiber content in amla also helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream.
- Skin and Hair Health: Amla is a popular ingredient in various skincare and hair care products due to its numerous benefits. The high vitamin C content helps in the synthesis of collagen, a protein essential for maintaining the skin’s elasticity and firmness. Amla’s antioxidant properties also help protect the skin from damage caused by UV rays and pollution. When it comes to hair, amla is known to strengthen hair follicles, promote hair growth, and prevent premature graying. It also helps in treating dandruff and other scalp conditions.
- Eye Health: Amla is beneficial for maintaining good eye health. The high vitamin A and C content, along with other antioxidants, help protect the eyes from oxidative stress and reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. Regular consumption of amla can also help improve vision and reduce eye strain.
- Weight Management: Amla is low in calories and high in fiber, making it an ideal addition to a weight management diet. The fiber content helps in promoting satiety, reducing overall calorie intake, and aiding in weight loss. Additionally, amla’s ability to improve digestion and metabolism further supports weight management efforts.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Amla has strong anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and asthma. The antioxidants in amla help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which is a major contributor to inflammation.
- Detoxification: Amla is known for its detoxifying properties, helping to cleanse the liver and flush out toxins from the body. The antioxidants and vitamin C in amla support liver function and enhance the body’s natural detoxification processes.
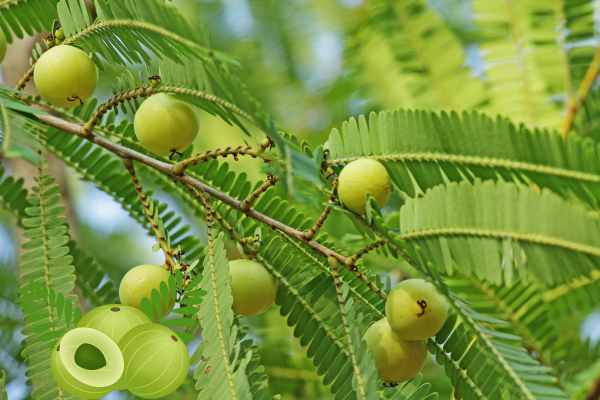

Uses of Indian Gooseberry
The versatility of Indian gooseberry is evident in its wide range of uses in culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic applications.
Culinary Uses
In Indian cuisine, amla is used in various forms, including fresh, dried, powdered, and as a juice. It is often added to chutneys, pickles, and preserves, providing a tangy and slightly bitter flavor. Amla is also used in traditional recipes such as amla murabba (a sweet preserve) and amla candy. The dried and powdered form of amla is commonly used as a spice or a natural supplement to boost nutritional intake.
Medicinal Uses
Amla is a cornerstone of Ayurvedic medicine, where it is used in various formulations to treat a wide range of ailments. Some of the common Ayurvedic preparations that include amla are:
- Triphala: A traditional Ayurvedic formulation consisting of three fruits: amla, haritaki, and bibhitaki. Triphala is known for its digestive and detoxifying properties.
- Chyawanprash: A herbal jam made with amla and various other herbs and spices. Chyawanprash is a powerful rejuvenative tonic that supports overall health and immunity.
- Amla Oil: Used in Ayurvedic hair care treatments to promote hair growth, prevent hair loss, and improve scalp health.
Cosmetic Uses
Amla is a popular ingredient in various cosmetic products due to its beneficial effects on skin and hair. Amla extract is used in shampoos, conditioners, hair oils, face masks, and creams. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties help improve skin texture, reduce signs of aging, and promote healthy hair growth.
Scientific Research on Indian Gooseberry
Numerous scientific studies have investigated the health benefits of Indian gooseberry, providing evidence to support its traditional uses and uncovering new potential applications. Some of the key research findings include:
- Antioxidant Activity: Studies have demonstrated that amla exhibits strong antioxidant activity, which can help protect against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Research has shown that amla has significant anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions.
- Antidiabetic Properties: Several studies have indicated that amla can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for managing diabetes.
- Cardioprotective Effects: Research has found that amla can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Antimicrobial Activity: Amla has been shown to exhibit antimicrobial activity against various pathogens, making it effective in preventing and treating infections.
Sustainability and Cultivation
Indian gooseberry is a hardy tree that thrives in a wide range of climatic conditions. It is commonly cultivated in India, particularly in the states of Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra. The tree is drought-resistant and can grow in poor soil conditions, making it an ideal crop for sustainable agriculture.
Amla trees start bearing fruit within 3-4 years of planting and continue to produce fruit for several decades. The fruit is harvested during the winter months, typically from November to February. Sustainable farming practices, such as organic farming and agroforestry, are encouraged to ensure the long-term viability of amla cultivation.
Conclusion
Indian gooseberry, or amla, is a remarkable fruit with a rich history, diverse nutritional profile, and numerous health benefits. Its traditional uses in Ayurveda and other medicinal systems have been validated by modern scientific research, highlighting its potential as a natural remedy for various health conditions. Whether consumed fresh, dried, powdered, or as a juice, amla offers a wide range of therapeutic and nutritional benefits that can enhance overall health and well-being. Its versatility in culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic applications further underscores its value as a truly remarkable fruit. As we continue to explore and understand the full potential of amla, it remains a shining example of nature’s bounty and a testament to the enduring wisdom of traditional medicine.